if you want to “ask a question†of the data in a relational database, what procedure do you use?
Relational Database Definition
A relational database stores and organizes data points that are related to one another. Based on the relational database model, a relational database presents data sets every bit a collection of tables and provides relational operators to dispense the data in tabular grade.
FAQs
What is a Relational Database?
Relational databases maintain data in tables, providing an efficient, intuitive, and flexible manner to store and access structured information. Tables, also known equally relations, consist of columns containing i or more data categories, and rows, also known as tabular array records, containing a prepare of data divers by the category. Applications admission data by specifying queries, which use operations such as project to place attributes, select to identify tuples, and bring together to combine relations. The relational model for database management was developed past IBM computer scientist Edgar F. Codd in 1970.
How practice Relational Databases Piece of work?
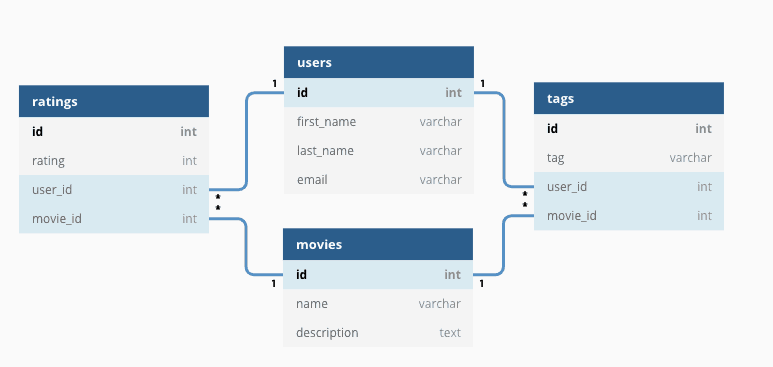
Relational databases provide an environment from which information can exist accessed or reassembled in a diversity of different means without needing to reorganize the database tables. Each table has a unique identifier, or master key, which identifies the information in the table, and each row contains a unique instance of data for the categories divers by the columns. For instance, the table might have a main cardinal of 'First Names' and rows with specific examples such every bit 'John, Paul, George and Ringo.'
The logical connectedness between dissimilar tables can then be established with the use of foreign keys - a field in a table that connects to the primary key data of some other table. Relational Database Management Systems often employ SQL or structured query language for gathering data for reports and for interactive queries. So in our example, Get-go Names might exist linked to a Role table with data roles of Lead Vocals, Bass Guitar, Drums and Lead Guitar.
How is Information in a Relational Database System Organized?
The relational model of the relational database separates logical data structures from physical storage structures, enabling database administrators to manage physical data storage without affecting admission to that information as a logical construction. The distinction also applies to database operations -- logical operations permit an application to specify the content it needs, and concrete operations decide how that information should exist accessed, and then carries out the task.
What are the Advantages of a Relational Database?
The main advantage of a relational database is its formally described, tabular structure, from which data can be hands stored, categorized, queried, and filtered without needing to reorganize database tables. Further benefits of relational databases include:
- Scalability: New data may be added contained of existing records.
- Simplicity: Circuitous queries are easy for users to perform with SQL.
- Information Accuracy: Normalization procedures eliminate design anomalies.
- Information Integrity: Potent data typing and validity checks ensure accuracy and consistency.
- Security: Information in tables inside a RDBMS can limit access to specific users.
- Collaboration: Multiple users tin can access the same database concurrently.
What is a Relational Database Management System?
A Relational Database Direction System is a tabular based collection of programs and capabilities that provides an interface between users and applications and the database, offering a systematic fashion to create, update, delete, manage, and think data. Virtually relational database management systems use the SQL programming language to access the database and many follow the Acrid (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) properties of the database:
- Atomicity: If any statement in the transaction fails, the entire transaction fails and the database is left unchanged.
- Consistency: The transaction must meet all protocols defined past the system -- no partially completed transactions.
- Isolation: No transaction has access to whatsoever other transaction that is unfinished. Each transaction is independent.
- Durability: Once a transaction has been committed, it will remain committed through the use of transaction logs and backups.
What is the Difference Betwixt a Relational and Non Relational Database?
Not Relational Databases, or NoSQL databases, store and organize data in means other than the tabular relations model used in relational databases. Where relational databases store data in rows and columns, have strict rules concerning data multifariousness and table relationships, and follow strict Acid properties, non relational databases offer a more flexible data construction based on the Base of operations (Basically Available, Soft state, Eventual consistency) model: Basically Available guarantees the availability of the information - there will be a response to any request, but without whatsoever consistency guarantee; Soft State guarantees that the state of the system could alter over time; and Eventual Consistency guarantees that the system volition eventually become consistent one time it stops receiving inputs.
Does HEAVY.AI Offer a Relational Database Solution?
Analyze relational data structures with the ability of HEAVY.AIDB, the foundation of the HEAVY.AI platform. HEAVY.AIDB is open source, SQL-based, relational, columnar and specifically developed to harness the parallel processing power of graphics processing units (GPUs) for interactive visual analytics. HEAVY.AIDB can query up to billions of rows in milliseconds, and is capable of unprecedented data ingestion speeds, making it the ideal SQL engine for the era of big, high-velocity information.
Source: https://www.heavy.ai/technical-glossary/relational-database
0 Response to "if you want to “ask a question†of the data in a relational database, what procedure do you use?"
Post a Comment